 | Adhaan (sometimes Azaan)
The "call" to prayer given before every obligatory salaah
in order to summon the people to the congregation.
|
 | Ahadith or Ahaadeeth
Plural of hadith.
|
 | Akhlaq or Akhlaaq
"Morals." Covers the nature, disposition, habits, and manners of a
person.
|
 | Allah (or Allaah)
- 
The name of the One and Only Almighty God, Creator of the Universe. It is
the essential name of God which has neither feminine, nor plural, nor has
ever been applied to anything other than the unimaginable Supreme Being.
There are also ninety-nine 'most beautiful names' of Allah,
like ar-Rabb (the Nourisher), al-Wadood (the Loving), ar-Rahmaan
and ar-Raheem (the Most Merciful, Most Beneficent), which signify
His different attributes.
|
 | 'Alim (pl. 'Ulama)
"Scholar." Used to refer to the scholars of the religion.
|
 | 'Amal (pl. A'maal)
"Action."
|
 | Amaanah
"A trust," or responsibility.
|
 | Amin or Ameen
"Faithful" or "Trustworthy." Al-Amin was the
title given to the Prophet Muhammad ( )
when a youth on account of his fair and honorable bearing which won the
confidence of the people. )
when a youth on account of his fair and honorable bearing which won the
confidence of the people.
|
 | Ansar or Ansaar
"The Helpers," the name given to the converts of Madinah,
in contrast to the Makkan followers who migrated to Madinah
and were called muhajirin, or migrants.
|
 | Arkaan (sing. Rukn)
The compulsory components of any act of worship without which it remains
invalid and unacceptable.
|
 | 'Aqiqah or 'Aqeeqah
A custom observed on the birth of a child: shaving the hair of the
infant's head on the seventh or another appointed day along with the
sacrificing of a sheep or goat to celebrate the occasion.
|
 | Asmaa-ul-Husnaa
"The Most Beautiful Names," of Allah.
|
 | Asmaa-ur-Rijaal
"The names of men." The study of (or a dictionary of) the
biography of those who handed down the hadith
of the Prophet Muhammad ( ). ).
|
 | 'Asr
The obligatory prayer offered midway between the early afternoon (Zuhr)
and sunset (Maghrib) prayers.
|
 | Dhuhr see Zuhr.
|
 | Dinar or Deenaar
A gold coin of ninety six grams.
|
 | Dirham
A silver coin.
|
 | 'Eid (-ul-Fitr or -ul-Adhaa)
"Festival." (1) 'Eid-ul-Fitr is the festival of
fast-breaking at the end of the month of Ramadaan;
(2) 'Eid-ul-Adhaa is the festival of sacrifice held on the 10th of
Zul-Hijjah (12th month of the Islamic calendar), in commemoration of the
story of the Prophet Ibrahim ( ) and
his family. ) and
his family.
|
 | Fajr
The obligatory pre-dawn prayer.
|
 | Hadith or Hadeeth (pl. Ahadith
or Ahaadeeth)
An account of the sayings, actions and any other characteristics of the Prophet
Muhammad  .
A hadith consists of two parts: the sanad, which is the chain
of names of people who have narrated the hadith through the
generations, and the matn, or the actual text and substance of the
report. Many books of hadith were compiled in the beginning eras of
Islam and thus we have a good record of how Muslims should be leading their
lives. .
A hadith consists of two parts: the sanad, which is the chain
of names of people who have narrated the hadith through the
generations, and the matn, or the actual text and substance of the
report. Many books of hadith were compiled in the beginning eras of
Islam and thus we have a good record of how Muslims should be leading their
lives.
The term hadith is slightly more general than the term sunnah
although the two are generally interchangeable. (Sunnah is not
usually applied to physical characteristics of the Prophet.)
See also sunnah.
Related articles: An
Introduction to Hadith.
|
 | Hafiz or Haafiz (sometimes Haafidh) (pl. Huffaaz)
(1) One who has committed the entire Qur'an to memory.
(2) In the context of hadith, it is a
comparative term referring to one who has expertise in this field regardless
of the number of ahadith he has memorized.
|
 | Hajj (, al-)
"(The) Pilgrimage" to Makkah performed in
the month of Zul-Hijjah, the 12th month of the Islamic calendar. It
is a duty to be performed by every adult Muslim once in a lifetime provided
one has the ability to do so.
|
 | Hijrah (, al-)
"(The) Emigration," applied to the migration of the Prophet of
Islam ( ) and his first followers
from Makkah to Madinah; the
beginning of the year in which this emigration took place (July 16, 622 C.E.)
is the starting point of the Muslim era, which follows
the lunar calendar. ) and his first followers
from Makkah to Madinah; the
beginning of the year in which this emigration took place (July 16, 622 C.E.)
is the starting point of the Muslim era, which follows
the lunar calendar.
|
 | Ibadah or Ibaadah
"Worship." (1) A general term for religious observance comprising
prayer, fasting, haj, payment of poor due, etc.; (2) Note that this term has very wide application in the
Islamic sense-- it includes not only ritual acts of worship such as the salah
but any action done by a human being for the pleasure of and in obedience to
the Almighty Allah. Thus, eating, drinking, and interacting with other
creatures and human beings with the proper intention and according to the sunnah
can count as ibadah and one will be rewarded for it.
|
 | 'Id see 'Eid.
|
 | Imam or Imaam (pl. A'immah)
"A leader." This word has slightly different meanings in different
contexts. For example, (1) the person who leads
the congregational salah is referred to as the
Imam; (2) the great
scholars of Islamic jurisprudence or hadith are
also given
the title, Imam.
|
 | Iman or Imaan (pronounced 'eemaan')
"Faith"-- Heartily acceptance and verbal confession thereof.
|
 | 'Isha or 'Ishaa
The obligatory prayer offered when twilight sets in.
|
 | Islam (or Islaam) - 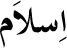
The literal meaning of Islam is "to entirely submit or surrender
oneself to someone else." The way of life followed by Muslims is
called Islam because it involves submitting oneself entirely and
completely to the orders of Allah in all aspects
of one's life in this world - physical, spiritual, social, political,
economic, etc. Islam has always been the way of life taught by all
the prophets that were sent to humanity, the last and final of which is the
Prophet Muhammad ( ). ).
Related articles: The
Religion of Peace.
|
 | Ka'bah
A rectangular building in Makkah, known as "the House of Allah"
and significant for a great many reasons.
See also Hajj, qiblah.
|
 | Kitab or Kitaab (, al-)
"(The) Book." A term used for the Qur'an and extended to all
the divinely revealed scriptures.
|
 | Koran
Incorrect transliteration of Qur'an.
|
 | Madinah (, al-)
"(The) City."
|
 | Madrasah (pl. Madaaris)
"School" or educational institution, especially imparting
religious knowledge.
|
 | Maghrib
The obligatory prayer offered just after sunset.
|
 | Makkah
City of birth of the Prophet Muhammad ( ). ).
|
 | Moslem
Incorrect transliteration of Muslim.
|
 | Muhajir or Muhaajir (pl. Muhajirin or
Muhaajireen)
|
 | Muhammad 
"The praised one." The name of the last and final prophet of Allah,
sent as a mercy for mankind, a warner and bringer of glad tidings to
humanity.
 -sallallaahu 'alayhi wa sallam - "peace and blessings of Allah
be upon him" is recited after pronouncing his name.
-sallallaahu 'alayhi wa sallam - "peace and blessings of Allah
be upon him" is recited after pronouncing his name.
Related articles: Muhammad,
The Ideal Prophet.
|
 | Muharram
The first month of the Islamic calendar.
|
 | Muslim (not Moslem) - 
A person who follows the way of life of Islam. It
literally means "one who has submitted or surrendered to someone
else." The feminine form of the word is Muslimah.
|
 | Nabi (pl. Ambiya) - 
“Prophet.” Used to refer to any of those special, sinless
human beings to whom Allâh revealed His guidance and charged them with
communicating that guidance to humanity. The first prophet was Prophet Âdam
(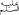 - ‘Alayhis-salâm - peace be upon him). The last prophet is the Prophet
Muhammad ( - ‘Alayhis-salâm - peace be upon him). The last prophet is the Prophet
Muhammad (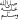 )-
no more prophets will come after him. Prophets are only those who were
specially chosen by Allâh. No one became a prophet out of his own efforts. )-
no more prophets will come after him. Prophets are only those who were
specially chosen by Allâh. No one became a prophet out of his own efforts.
|
 | Qiblah
"Direction" of the Ka'bah (in Makkah),
faced when performing salaah and other acts of
worship.
|
 | Qur'an (or Qur'aan, not Koran)
The Book revealed to the Prophet Muhammad 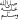 from Allah. The Qur'an is the last and final revelation that will come from
God until the Day of Judgment. Since the time of its revelation, not a
single letter or word of the Qur'an has been lost or altered and it will
remain so until the Last Day. The Qur'an contains guidance for every sphere
of human life and is complemented by the Hadith.
from Allah. The Qur'an is the last and final revelation that will come from
God until the Day of Judgment. Since the time of its revelation, not a
single letter or word of the Qur'an has been lost or altered and it will
remain so until the Last Day. The Qur'an contains guidance for every sphere
of human life and is complemented by the Hadith.
|
 | Rak'ah (pl. Rak'aat)
A unit of prayer consisting of recitation while standing, a genuflexion, and
two prostrations.
|
 | Ramadan or Ramadaan (sometimes Ramadhan
or Ramazan)
The ninth month of the Islamic year, when Muslims keep fast from dawn to
sunset during the whole month.
|
 | Rasool (pl. Rusul)
- 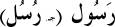
lit. “a messenger” or “an envoy.” Used almost interchangeably
with Nabi (prophet). The slight difference is that a
Rasool is a prophet who was sent with a book and a Shari'ah (code of
divine laws), for example, the Prophets Műsâ, ‘Îsâ and Muhammad
(peace
be upon them all). Muslims believe in and accept all the prophets and
messengers sent by Allâh. In terms of the divine law, however, the Shari'ah
of the Prophet Muhammad ( )
has overridden and/or abrogated the previous revelations and it is this code
of law which is followed by the Muslims from now until the Day of Judgment. )
has overridden and/or abrogated the previous revelations and it is this code
of law which is followed by the Muslims from now until the Day of Judgment.
|
 | Rukn see Arkaan.
|
 | Sahaabah or Ashaab (sing. Saahib)
"Companions", especially those of the Prophet Muhammad ( ):
anyone who accepted Islam and saw the Prophet during his lifetime. ):
anyone who accepted Islam and saw the Prophet during his lifetime.
 -Radiyallaahu 'anhu
/ 'anha / 'anhum - "Allah be pleased with him/her/them" is
recited after mentioning the name of the companion of the Prophet Muhammad ( -Radiyallaahu 'anhu
/ 'anha / 'anhum - "Allah be pleased with him/her/them" is
recited after mentioning the name of the companion of the Prophet Muhammad ( ). ).
See also tabi'i.
|
 | Salah or Salaah (pl. Salawaat)
(1) A special form of worship performed by standing before Allah
facing the Qiblah, with hands crossed on the
belly, in the mosque or at home, reciting the Qur'an,
praising Allah’s greatness, bowing to Him in respect
and putting the forehead on the ground to show humility to Him. There are
five obligatory prayers to be offered every day and night: Fajr,
Zuhr, 'Asr, Maghrib,
and 'Isha. (2)
|
 | Sha'baan
The eighth month of the Islamic year.
|
 | Shari'ah or Sharee'ah
(1) The Divine law based on the teachings of the Qur'an and
the Sunnah of the Prophet Muhammad ( ).
(2) Also used to refer to the codes of law given to previous prophets. ).
(2) Also used to refer to the codes of law given to previous prophets.
|
 | Sunnah (pl. Sunan)
"Saying," or "a custom." The sunnah represents an
authentic saying, act or tacit approval of the Prophet Muhammad ( ). ).
See also hadith.
|
 | Surah (pronounced 'soorah')
A term used exclusively for the chapters of the Qur'an,
of which there are 114 in number.
|
 | Tabi'i or Taabi'ee (pl. Tabi'een)
"Follower." Those Muslims in the era of the companions of the
Prophet Muhammad ( )
or who saw the Sahaabah when they had
accepted Islam but not the Prophet (although they may have been alive during
his time). )
or who saw the Sahaabah when they had
accepted Islam but not the Prophet (although they may have been alive during
his time).
|
 | 'Ulama
Plural of 'Alim.
|
 | Ummah
"Nation." Commonly, the collective body of Muslims all over
the world is referred to as the Muslim Ummah or the Ummah of
Muhammad ( ). ).
|
 | Zakah or Zakaah
Poor due incumbent upon every adult Muslim who possesses a specified
amount of savings for the period of a year.
|
 | Zuhr (sometimes Dhuhr)
The obligatory prayer observed between midday and late afternoon. |

![]()